WHY STRUCTURAL STEEL PROTECTION?
Steeel loses its mechanical strength by 50 % if exposed to the heat in the event of a fire and hence needs to be protected
Two types of protection is possible for steel
1. Paint /spray system
2. Board protection by boxing of steel members
A. Steel structures application in a modern building design.
B. Therefore, structural steel protection is required to preserve the stability of the building in the event of fire.
C. In other words, the building shall be designed and constructed so that, in the event of fire, its stability will bemaintained for a reasonable period. Ref section B3, Approved Doc B, UK
D. In order to meet this requirement, the load-bearing elements of the structure of the building must be capableof withstanding the effects of fire for an appropriate period without loss of stability.
FIRE TESTING METHODS:
The Building Regulations require certain elements of structure to have fire resistance for a specified minimum period of time. The amount of fire protection to achieve this depends on the following:
Duration of fire resistance specified
Type of protection used
Perimeter of the steel section exposed to fire
Shape and size of the steel section
To determine how these factors affect fire resistance, all Promat products and systems have been tested at NAMAS ccredited laboratories and witnessed and approved by a representative from the Fire Research Station.Tests in accordance with BS476: Part 21 has been performed on loaded beams and columns clad with fire protection material. Steel surface temperatures are monitored with thermocouples to assess the performance of the cladding, since steel fully stressed in accordance with BS 449 or BS 5950, Part 1, begins to lose its design margin of safety at temperatures around 550oC.A range of unloaded sections have also been tested to obtain data for calculating analytically, with the aid of a computer, xactly how much protection is needed for the most common steel sections and for providing fire resistance for different time periods.
These and other tests have also demonstrated the ability of the cladding to remain in place, commonly termed as the ‘stickability’ of the material, for the maximum duration for which protection may be required.
Hp/A SECTION FACTOR
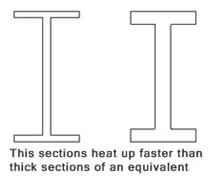
The degree of fire protection depends on the Hp/A section factor for the steel section. The Hp/A factor is a function of the area of the steel exposed to the fire and the mass of the steel section. The higher the Hp/A, the faster the steel section heats up, and so the greater the thickness of fire protection material required, also of relevance is the steel section itself, a thick section of steel will take longer to heat up than a thinner section, therefore it follows that where you have two steel sections of identical overall dimensions, but where the flange and web of one section is thicker material than the other, then the thicker section would generally require a lower level of protection in order to provide the same fire resistance period.
Comparison of Board Vs Sprays
| Boards | Spray | ||
| 1 | Technical | The thickness of the board is assured | The thickness is not really uniform all through. |
| 2 | Life | Has a very long life | Has a short life. |
| 3 | Fixing | Has to be fixed with technical know how. It does not take time to fix. | Easy fixing but takes a lot of time |
| 4 | Moisture/temperature | Does not effect on boards. | Can lead to problem while on site depending if the weather condition is cold. |
| 5 | Adhesives | Adhesiveness is required. | Lack of proper application could reduce the effect of adhesiveness. Specially in case of re-spraying. |
| 6 | Cost | Cost effective, especially in long run. | Inexpensive in the short run but requires additional costs during re-spraying and maintenance |
Comparison of Board Vs Paints
| Boards | Paint | ||
| 1 | Technical | The thickness of the board is assured | The thickness is not uniform. |
| 2 | Life | Has a very long life | Has a short life. |
| 3 | Fixing | Has to be fixed with technical know how. It does not take time to fix. | Easy fixing but takes a lot of time. |
| 4 | Moisture/temperature | Does not effect on boards. | Can lead to problem while on site depending if the weather condition is cold. |
| 5 | Adhesives | Adhesiveness is required. | Lack of proper application could reduce the effect of adhesiveness. Specially in case of re-spraying. |
| 6 | Cost | Cost effective, especially in long run. | Very Expensive. |





















